Material-handling Equipment Used in Logistics and Distribution
1. Types of Material-handling Equipment
Material-handling equipment is any hardware that is used to hold, position, weigh, transport, elevate, manipulate, or control the flow of raw materials, work in process, or finished goods.
This encompasses equipment that can range from the smallest manufacturing jig to the largest transfer truck used for transport.
The Material Handling and Management Society has divided material-handling equipment into the following categories:
- Conveyors
- Cranes, elevators, and hoists
- Positioning, weighing, and control equipment
- Industrial vehicles
- Motor vehicles
- Railroad vehicles
- Marine carriers
- Aircraft
- Containers and supports
The scope here is the discussion of material-handling equipment that applies to logistics and distribution. Therefore, we can narrow these categories down to the following:
- Conveyors—all equipment that moves material/loads between two places in a continuous manner. The equipment exists along the entire path used.
- Industrial trucks—any non-highway equipment that is used to move material / loads in a batch manner.Typically these span a large area.
2. Conveyors
Conveyors exist that can move a variety of items, from sand and gravel to cartons of finished goods, all the way to pallets of cartons of finished goods. There are two main categories of conveyors:
- Bulk material-handling conveyor—these include bucket, pneumatic, screw, trough, and vibratory designs. These move material such as loose sand and gravel.
- Unit load-handling conveyor—these include chute, wheel, roller, belt, live roller, and many others. This conveyor type is used for moving finished goods in bags, cartons, totes, drums, and so on.
Because in distribution we are almost always dealing with finished goods, the discussion here will be about unit load-handling conveyors. Unit load conveyors include roller, wheel, belt, live roller, chain, and others. Conveyors, of the required type, are used to move a unit load over a fixed path between two or more points. The Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association defines a conveyor as
A horizontal, inclined or vertical device for moving or transporting bulk material or objects in a path, predetermined by the design of the device and having points of loading and discharge, fixed or selective . . .
Most conveyors found in distribution systems will fall into one of the following classifications:
- Gravity conveyor
- Chute
- Ball transfer
- Wheel
- Roller
- Powered conveyor
- Belt
- Live roller
- Accumulation
- Sortation systems
- Turntable
- Transfer car
2.1 Gravity conveyor
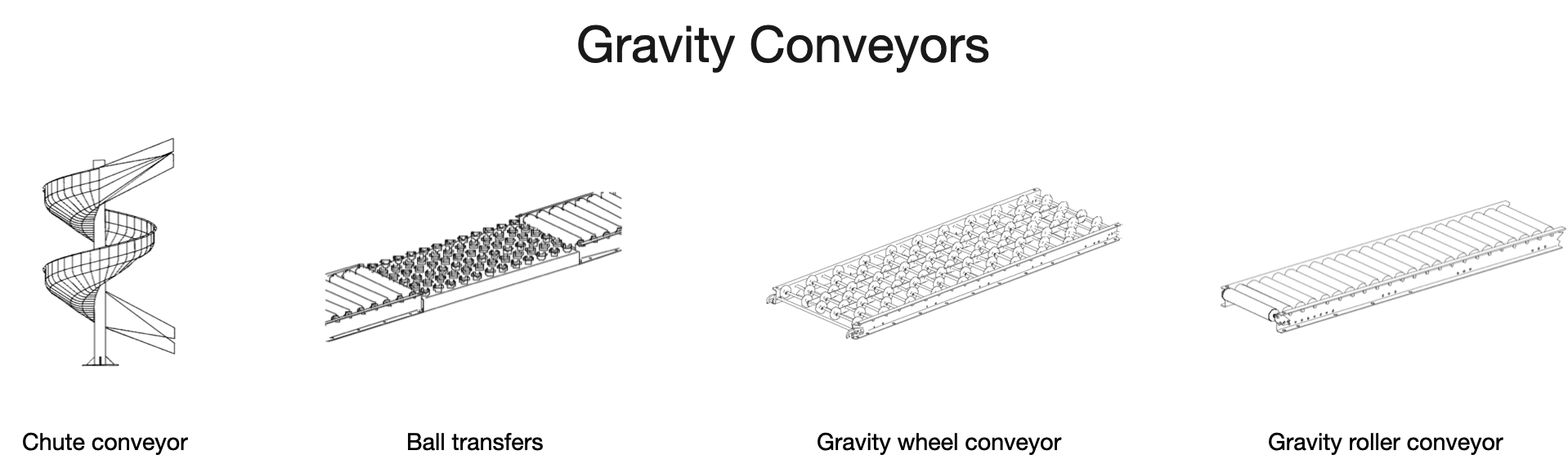
| Types | Applications |
|---|---|
| Chute conveyor | Used to move goods by sliding them |
| Ball transfers | Used to reposition loads manually |
| Gravity wheel | Used to move cartons in portable applications |
| Gravity roller | Used to move higher variety of loads, less portable |
Chute conveyor
A chute conveyor is used to change the position and elevation of a load by having the load slide from top to bottom (entrance to exit).
Common applications: Short distances and for durable loads that can handle the sliding and bumping around.
-
Pros: easy to use and relatively inexpensive to apply.
-
Cons: hard to control the speed of the loads and sometimes has jam.
Ball transfer
A ball transfer conveyor is an array of steel balls mounted in holders that are then mounted on a sheet metal bed or support.
Common applications: Scale operations such as parcel post / UPS / RPS. Another application is a packing station where a pop-up roller ball transfer can be used to assist movement of heavier loads.
-
Pros:
- allows the unit load to be moved easily into position.
- can be dropped below the work surface causing the unit load to rest securely on the surface and not move around.
-
Cons:
- can be hard on the bottom of the unit load because of the point-type loading.
- soft loads do not work well on roller ball transfers.
Gravity wheel
Gravity wheel conveyors are most often referred to as skate wheel conveyors because the wheels look like old fashioned steel-wheeled roller skates. A common distribution application is in picking operations and in loading / unloading trailers.
Common applications: Picking operations and loading / unloading trailers.
-
Pros:
- easily handled and installed.
- can quickly joined to make any length required, or shortened as needed.
- also come in curved sections.
- good for loads with hard, durable bottom surfaces.
-
Cons: bags or other soft items generally do not flow well on skate wheel conveyors.
2.2 Powered Conveyor
A powered conveyor is a conveyor that is motorized. Powered conveyors can be designed to convey just about anything.
| Types | Applications |
|---|---|
| Belt conveyor | Used for inclines / declines and pure transportation |
| Flat belt conveyor | Allows adjustable drive pressure |
| V belt conveyor | Allows power to rollers through curves |
| Cable-driven | Used in more demanding environments |
| Line shaft | Very flexible drive allowing straights, curves, junctions, and right-angle transfers |
| Chain-driven | Allows for better load control and heavier loads |
| Accumulation: Continuous | Used for durable product in uniform sizes |
| Zero Pressure | Used for fragile, less durable goods in various sizes |